Table of contents
Understanding Common Types of Bolts and Nuts in Construction Machinery
In heavy machinery, bolts and nuts, though small in size, bear extremely high loads. Excavators and bulldozers operate in complex environments, including vibration, impact, high temperatures, and abrasive conditions. The quality of bolts and nuts directly affects equipment safety, reliability, and lifespan. Common bolts used in construction machinery include sprocket bolts, track shoe bolts and nuts, and high-strength bolts, each serving a specific purpose.
1. sprocket bolts
Sprocket bolts are mainly used to secure the drive sprocket to the track chain, bearing high torque and impact loads from power transmission. They are usually made of high-strength alloy steel and undergo heat treatment to enhance tensile strength and fatigue resistance. Surface treatments such as zinc plating, blackening, or chrome plating improve corrosion resistance, making them suitable for muddy, wet, or high-temperature conditions.
2. track shoe bolts and nuts
Track shoe bolts and nuts are used to fasten the track shoes of bulldozers or excavators, ensuring the track is tightly secured and can withstand operational impacts. Bolts are typically made of high-strength carbon steel or alloy steel, and nuts may include locking features such as nylon inserts or elastic washers to prevent loosening from vibration. Proper selection of these bolts and nuts is critical for stable equipment operation.
3. High-strength bolts and specialty nuts
For critical load-bearing parts, such as the main frame or hydraulic arm connections, using Grade 8.8–12.9 high-strength bolts and wear-resistant nuts significantly improves the machine’s tensile and shear capacity. In high-humidity, high-abrasion, or corrosive environments, corrosion-resistant or coated bolts can extend service life and reduce maintenance frequency.
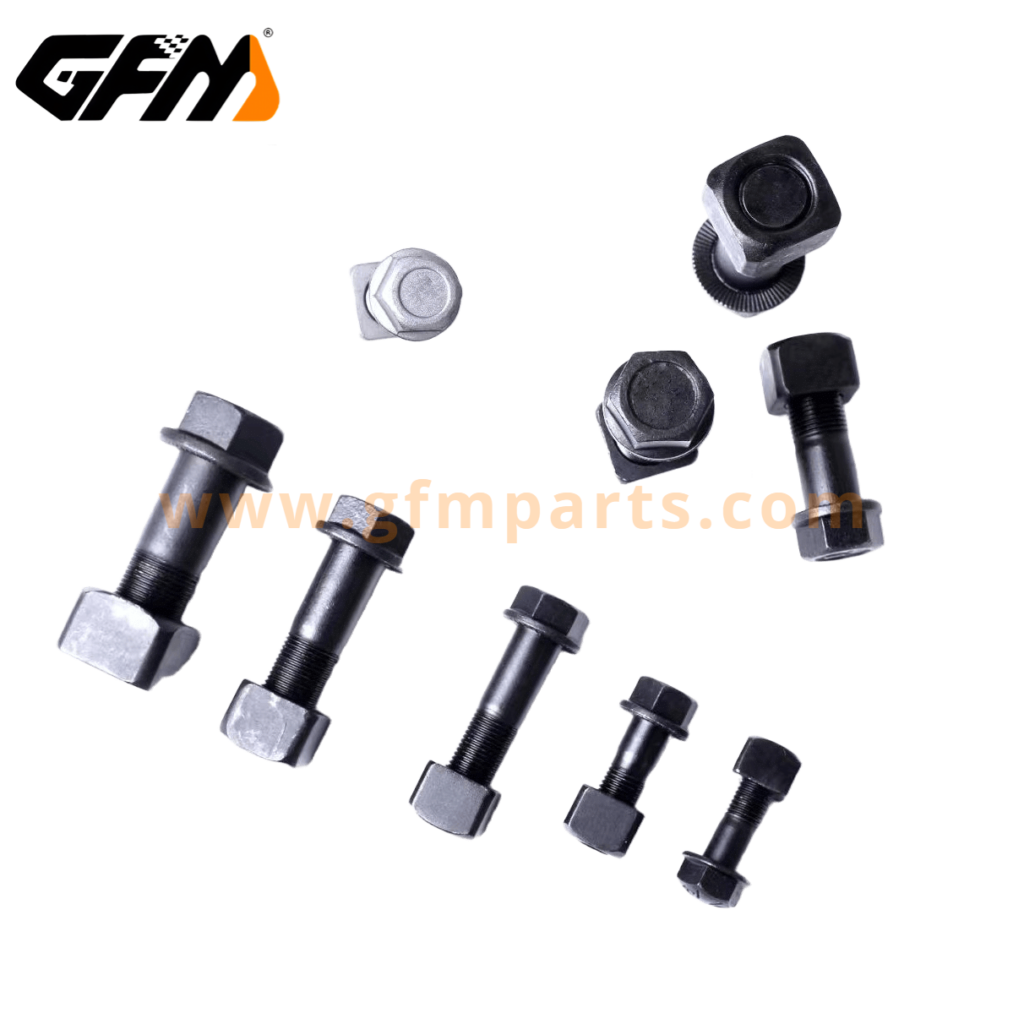



How to Choose Suitable sprocket bolts and track shoe bolts and nuts
Selecting bolts and nuts is not just about size or thread type, it must consider machine model, operational load, and environmental conditions.
1. Strength grade and specifications
- Commonly used high-strength bolts for excavators and bulldozers are Grade 8.8, 10.9, or 12.9.
- Bolt length and diameter should match the track shoe or sprocket hole spacing, ensuring full engagement with the nut.
- Thread specifications must match exactly to prevent loosening or damage.
2. Wear resistance and fatigue strength
- sprocket bolts and track shoe bolts and nuts are subjected to continuous impact and vibration, so heat-treated or surface-hardened products are recommended.
- Heat-treated Grade 10.9 bolts have significantly longer fatigue life, ensuring reliability under heavy-duty conditions.
3. Material and environmental compatibility
- For wet or muddy environments, corrosion-resistant materials or coated bolts are preferred.
- For high-temperature operations, heat-resistant alloy steel bolts prevent thread loosening due to thermal expansion.
- Incorrect selection can result in bolt breakage, track loosening, or even equipment downtime.
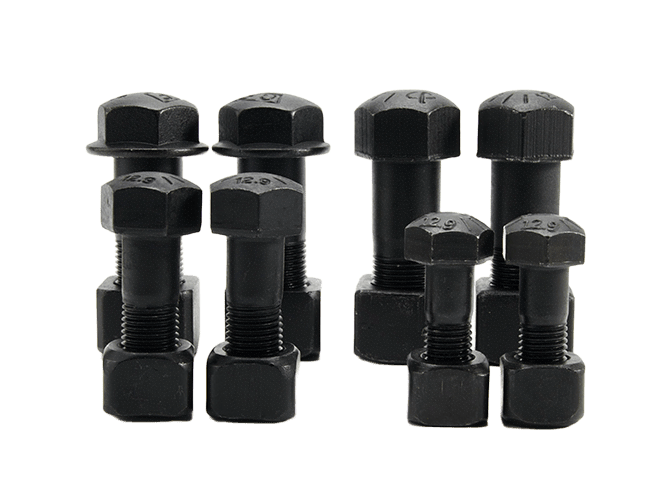

Best Practices for Installing Bolts and Nuts
Even with proper bolt selection, incorrect installation can reduce performance.
1. Use torque wrenches and torque tools
- Each bolt has a recommended torque value provided by the equipment manufacturer.
- Cross-diagonal tightening ensures even force distribution on multi-bolt connections.
- Regular calibration of torque tools ensures accurate installation.
2. Thread-locking compounds and lubricants
- In high-vibration environments, thread-locking compounds (e.g., Loctite 243 or 262) prevent loosening.
- Lubricants or anti-rust oils reduce friction, making torque control easier and preventing thread damage from over-tightening.
3. Anti-loosening measures and inspection
- Elastic washers, nylon-lock nuts, or double-nut designs enhance fastening reliability.
- After installation, perform initial operational checks to ensure bolts remain tight and recheck during early operation.
Maintenance and Inspection of Excavator and Bulldozer Bolts and Nuts
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing failures during prolonged operation.
1. Periodic inspection and replacement cycles
- It is recommended to inspect track shoe bolts and sprocket bolts every 250–500 working hours or follow the manufacturer’s manual.
- Replace bolts showing wear, corrosion, or loosening immediately.
- High-strength bolts generally have a service life of 1–2 years, but in high-vibration or corrosive conditions, replacement intervals should be shorter.
2. Common failure types and causes
- Loosening: Caused by vibration or insufficient torque.
- Breakage: Caused by insufficient material strength, fatigue, or overload.
- Wear and corrosion: Caused by long-term friction or exposure to mud, water, and chemicals.
3. Practical maintenance tips
- Mark key bolts to easily check for loosening.
- Record replacement and inspection times along with torque values to maintain a maintenance log.
- Keep threads clean to prevent mud or oil from affecting tightness.

Common Issues and Solutions
In actual operations, bolt and nut issues are frequent but can be effectively addressed with proper methods.
1. Loosening
- Solution: Use locking nuts, washers, or thread-locking compounds, and follow the recommended torque during installation.
- Prevention: Perform regular checks after installation, especially during initial operation.
2. Bolt breakage
- Solution: Replace with high-strength bolts and check load conditions and usage practices.
- Prevention: Use Grade 10.9 or 12.9 bolts suitable for operational loads and avoid overloading.
3. Wear or corrosion
- Solution: Replace worn bolts promptly and use corrosion-resistant coatings.
- Prevention: Keep bolts clean, apply regular lubrication, and perform anti-rust treatment as needed.
| Get a quick free quote | Email: henry@gfmparts.com | Whatsapp: +86 17705953659 |
Although small, bolts and nuts for excavators and bulldozers are crucial for safe and efficient machine operation. By selecting proper sprocket bolts and track shoe bolts and nuts, combined with correct installation and regular maintenance, service life can be significantly extended, work efficiency improved, and downtime reduced. The practical advice in this article helps operators, maintenance engineers, and procurement personnel better manage bolts and nuts, ensuring each excavator and bulldozer operates safely and efficiently.