If you have ever stood next to a bulldozer and watched it dig holes on a construction site, you might think it is an almost invincible beast. But do you know? No matter how powerful a bulldozer is, if the undercarriage parts are damaged, it will become powerless. The undercarriage, like human legs, is the core structure for the bulldozer to maintain balance, travel and load, and the condition of its parts is directly related to construction efficiency, safety and operating costs.
Judgment of whether the dozer undercarriage parts need to be replaced is not just the task of maintenance engineers. It is a core skill that must be mastered for equipment managers, construction managers and even business owners. On the one hand, wrong judgments may cause small problems to become major failures, affect construction progress and even cause safety accidents. On the other hand, replacing undamaged parts in advance will increase unnecessary operation and maintenance costs. Therefore, mastering scientific and practical judgment criteria is not only a need for equipment maintenance, but also the key to reducing costs and increasing efficiency for enterprises.
Table of contents
- Basic composition and working principle of bulldozer undercarriage
- 6 major judgment criteria for replacing bulldozer undercarriage parts
- Common types and identification methods of parts wear
- Methods for undercarriage inspection using professional tools
- How does the working environment of bulldozers affect the replacement cycle of parts
- Correct process and precautions for parts replacement
Basic composition and working principle of bulldozer undercarriage
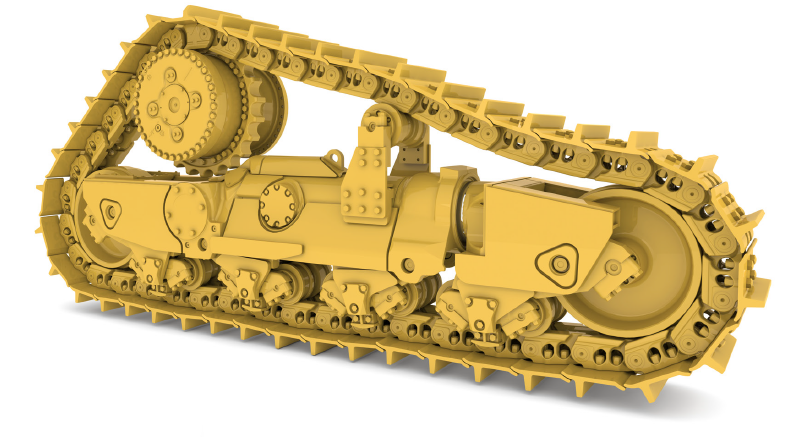
The undercarriage system of a bulldozer is the core of its walking device, mainly including: track shoe, track link assembly, track link, bottom roller, carrier roller, idler roller, sprocket, etc. These parts together constitute the basic structure for the bulldozer to maintain stability and advance in various complex terrains.
Track shoe: It is a component that is in direct contact with the ground. It provides grip and bearing capacity. It is usually made of high-strength manganese steel and is connected to the track link by bolts.
Track link: It connects the track shoe and forms a closed track system that can be bypassed. It relies on the pin shaft and bushing to achieve flexible rotation.
Track roller and carrier roller: They bear the lower and upper loads of the bulldozer during operation, respectively, so that the track can run smoothly and maintain its tension state.
Idler roller: Its function is to guide the track to maintain a straight walking direction, and at the same time, it cooperates with the tensioning device to adjust the tightness of the track.
Sprocket: Located at the rear of the undercarriage, it outputs torque by connecting to the engine power system to drive the track to roll.
The entire undercarriage system not only supports the weight of the whole machine through the precise coordination of these parts, but also realizes the complex actions of the bulldozer such as steering, driving, and climbing. Any abnormality in any of these parts will affect the stability and operation capacity of the whole machine.
Are you looking for quality bulldozer parts at the best price? You have come to the right place. We are committed to providing excellent products and offering the best value to our customers. Your satisfaction is our motivation. Send an email to henry@gfmparts.com now and our bulldozer undercarriage experts will be happy to serve you.
6 major judgment criteria for replacing bulldozer undercarriage parts
After understanding the composition of the undercarriage, the next thing we need to focus on is how to judge whether these key parts need to be replaced. The following are 6 judgment criteria generally recognized by engineers and mechanical equipment managers:
Obvious signs of wear
Any metal part will wear out during long-term operation, but the wear forms of different parts are not the same. For example, the central teeth of the track plate will be “thinned” after wear, and the contact surfaces inside and outside the chain links may also become smooth or even concave due to friction. When such wear has affected the structural strength or contact accuracy of the parts, replacement should be considered.
Too large a gap
The gap between the link pin and the bushing is a key indicator for determining whether the track is loose. Under normal circumstances, this gap should be strictly controlled at the millimeter level, but if the track is found to have chain skipping, slipping, deflection, etc. in actual use, it mostly means that the gap has exceeded the normal range.
Cracks or partial fractures
Cracks or obvious fractures appear on the surface of the parts, especially when the track plate is impacted during construction and a “Y”-shaped crack appears, indicating that its strength is seriously insufficient. Continued use may cause overall structural fracture or construction site accidents, and must be replaced immediately.
Deformation or irregular shape
The sprocket and the supporting wheel often produce eccentric wear or wheel rim deformation due to continuous force or being squeezed by stones. If the wheel body is found to be deflected or the tooth shape is abnormal, it may cause the track to run unsteadily and should be replaced.
Abnormal sound
When the undercarriage makes abnormal noises while moving, such as “clicking”, “clicking” or metal impact, it is often a precursor to wear, loosening or even breakage of internal parts. At this time, you need to stop and check immediately.
The service life has reached the design limit
Different parts have different design lifespans. Generally speaking, the service life of bulldozer undercarriage parts is between 1500 and 4000 hours. If the recommended service life has been reached or exceeded, even if there is no serious failure, it should be replaced in a planned manner to prevent sudden downtime.
Common types and identification methods of parts wear
In actual construction sites, the wear forms of bulldozer undercarriage parts are varied, and the wear characteristics of different parts are different due to their different positions and force modes. The following are several typical wear types and identification methods:
Groove wear: mainly occurs in track chain links, bushing outer surfaces, support wheel rims and other parts. This type of wear is caused by surface erosion caused by particles entering the contact surface, generally accompanied by metal powder or rust marks.
Asymmetric wear: Common on sprockets and Sprockets, with severe wear on one side of the wheel rim and almost intact on the other side. This is caused by deviation of the track, misaligned guidance or uneven site terrain.
Raised wear: If there is a noticeable bulge on the contact surface of the chain link, it may be caused by insufficient lubrication or rust on the pin. At this time, the chain link is not flexible, affecting the efficiency of the whole machine.
Scratches and tears: The edge of the track plate is scratched by foreign objects, and the support wheel guard is damaged. Although these details seem harmless, they may be a precursor to bigger problems.
Through regular cleaning and inspection, manual measurement, and observation of the symmetry of parts, these early damages can be quickly identified and countermeasures can be taken in advance.

Methods for undercarriage inspection using professional tools
It is obviously difficult to find some hidden problems by naked eye inspection alone. Therefore, the use of professional inspection tools can greatly improve the accuracy of judgment. The following are several common and practical tools and their use methods:
Vernier caliper: It can be used to measure the degree of wear of pins, bushings, chain link height and other parts with an accuracy of up to 0.02mm, which is suitable for daily maintenance.
Chain link measuring device: a tool used to measure whether the chain link pitch exceeds the limit, and to judge whether to replace it by comparing the standard pitch with the actual data.
Track tensioning gauge: used to measure the vertical spacing between the track and the supporting wheel. If the value deviates from the standard range, it means that the tensioning mechanism has failed.
Magnetic crack detector: suitable for finding tiny cracks on the metal surface, it can detect hidden cracks that are difficult to detect with the naked eye, and is a tool for judging track plate cracks.
It is recommended that equipment management personnel use the above tools regularly to conduct a full undercarriage inspection once a month, and record and archive the inspection data for subsequent comparative analysis and replacement decisions.
How does the working environment of bulldozers affect the replacement cycle of parts
The use environment of bulldozers varies greatly. Different terrains and work contents will significantly affect the wear rate and replacement cycle of undercarriage parts:
Hard rock/gravel terrain: The ground is hard and accompanied by sharp stones, which can easily cause track plate fractures and chain link tooth collapse. It is generally recommended to check once every 1000 hours.
Wetland/muddy environment: Mud adhesion accelerates the rust of parts and lubrication failure, especially the pin shaft and supporting wheel, which need more frequent lubrication and inspection.
Building demolition site: Concrete fragments will get stuck between the track and the wheel set, causing asymmetric wear, and should be cleaned after daily operation.
High temperature or cold areas: High temperature will accelerate the oxidation of lubricating oil, and cold will cause metal brittle cracking. The maintenance frequency and method should be adjusted according to the season.
Therefore, the replacement cycle in the factory manual should not be blindly copied, but a personalized maintenance plan should be formulated in combination with the actual working environment.

Correct process and precautions for parts replacement
Replacing bulldozer undercarriage parts is not a trivial matter. Improper operation will cause new problems. The following are general replacement processes and precautions:
Stop and turn off the power and set up safety warning signs: Make sure the equipment is completely turned off and there is no pressure residue to prevent construction personnel from entering the danger zone by mistake.
Unload track tension: Loosen the idler roller tensioning device to relax the track tension for easy removal of parts.
Use appropriate lifting tools: Some parts such as crawler chain links and Sprockets are heavy and need to be equipped with lifting chains or forklifts to assist in disassembly and assembly to avoid crushing accidents.
Check the accessories one by one: For example, when replacing chain links, the pins and bushings should be checked simultaneously, and replaced together if necessary to ensure overall coordinated operation.
Tighten the bolts strictly according to the torque: Use a torque wrench to tighten according to the manufacturer’s recommended torque to prevent the bolts from falling off or damaging the threads.
Perform a short-distance test run after replacement: Run for 5 to 10 minutes under no-load conditions to check for abnormal noise, chain jumping, offset and other problems.
A safe and standardized replacement process not only ensures the personal safety of construction workers, but also extends the service life of new parts.
| Get a quick free quote | Email: henry@gfmparts.com | Whatsapp: +86 17705953659 |
As a representative of heavy equipment, the high-intensity and high-load working environment of bulldozers is destined to the inevitable loss of bulldozer parts. However, as long as we master the scientific judgment criteria, use appropriate detection tools, and conduct regular inspections and maintenance in combination with actual working conditions, replacing parts is no longer a “post-repair” but a “pre-prevention”.
As a brand that has long focused on the research and development and manufacturing of construction machinery undercarriage parts, GFM has been committed to providing high-precision, high-wear-resistant, and highly adaptable parts products and services. We also hope that the content of this article can provide truly useful judgment basis for equipment managers and on-site construction workers, help everyone grasp the maintenance opportunity, avoid unexpected downtime, and ensure the smooth completion of each construction task.
Next time, when you approach a bulldozer, perhaps you will understand more about its silence and power, and how much wisdom you can see or not see in the parts judgment and maintenance.








