As heavy engineering machinery, excavators operate for a long time, under high load and in complex environments. As one of its key components, the oil tank directly affects the working performance of the hydraulic system and the life of the equipment. Dirt inside the oil tank will not only reduce the quality of the oil, affect the lubrication and heat dissipation effects, but also may cause system blockage, increased wear and other problems.
GFM ekskavatör alt takım parçaları üreticisi has more than ten years of industry experience and is committed to providing customers with high-quality ekskavatör alt takım parçaları and providing customers with industry knowledge for use.
Multi-dimensional causes of dirt in excavator oil tank
Mechanical wear and metal particle deposition
During long-term operation, the inner wall and internal parts of the oil tank are slightly worn due to friction, vibration and other factors, and the generated metal chips and wear particles are often suspended in the oil. As time accumulates, these particles will gradually settle at the bottom and inner wall of the oil tank, forming aggregates of tiny particles, and further react chemically with other components in the oil to transform into dirt that is more difficult to remove.
Oil aging, oxidation and additive decomposition
Oil is prone to oxidation under high temperature, high pressure and continuous operation. The oxidation products are usually colloidal and react with additives to cross-link, resulting in increased oil viscosity. This change not only reduces the lubricity of the oil, but also makes it easy for the oxide to adhere to the inner wall of the oil tank, forming a layer of sludge that is difficult to remove.
Water mixing and emulsification
There are often problems of water mixing caused by environmental humidity, rainwater infiltration and improper operation at the operation site. When water comes into contact with oil, it will cause emulsification. After the oil and water are emulsified, the water is dispersed in the oil in the form of tiny droplets, which not only affects the fluidity of the oil, but also accelerates metal corrosion, and at the same time promotes the precipitation of impurities to form a layer of dirt that is difficult to dissolve.
Foreign impurities and failure of the filtration system
Impurities such as dust, sand and gravel in the external environment of the oil tank are easy to enter the oil tank when the filtration system fails or is not replaced in time. After long-term accumulation, these foreign substances combine with other components in the oil, not only forming sediments, but also may block the oil circuit, affecting the working efficiency of the entire hydraulic system.
Effect of ambient temperature and pressure changes
Severe changes in temperature and pressure can change the physical properties of the oil. For example, the viscosity of the oil increases at low temperatures, while the oxidation of the oil is accelerated at high temperatures. Repeated temperature shocks and pressure fluctuations can easily form stress concentration areas inside the oil tank, which are more likely to deposit pollutants, thereby exacerbating the formation of oil tank dirt.
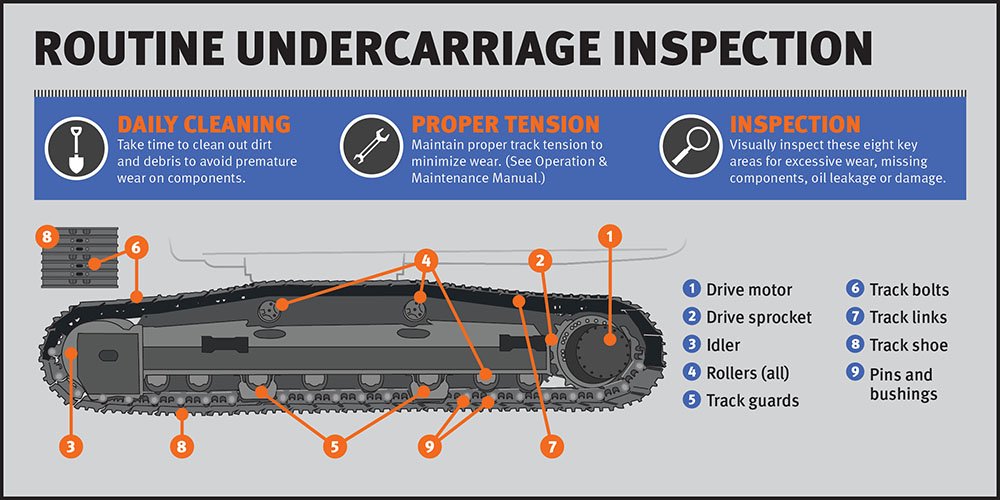
Multi-angle discussion on the removal of excavator oil tank dirt
In response to different causes and degrees of pollution, the industry has formed a variety of oil tank cleaning technologies. Each method has its applicable scenarios and advantages and disadvantages, and the selection should be combined with the actual situation of the equipment and the characteristics of the oil.
Regular oil drainage and oil change cleaning method
Principle and advantages:
- Regularly draining part or all of the oil in the oil tank and replacing it with high-quality new oil can effectively dilute and remove suspended impurities and reduce the possibility of sediment formation. This method is simple to operate and low in cost, and is suitable for situations where the oil pollution is relatively light.
Application details:
- Monitoring oil indicators: Use online or laboratory testing of the acid value, viscosity and impurity content in the oil to formulate a reasonable oil change cycle.
- Pay attention to sealing and environmental protection: During the oil discharge process, oil leakage should be prevented to ensure that waste oil is treated in accordance with environmental protection requirements.
Mechanical brushing and ultrasonic assisted cleaning
Principles and advantages:
- Mechanical brushing uses special brushes or automated cleaning equipment to directly physically rub the inner wall of the oil tank to remove the attached dirt; while ultrasonic cleaning uses high-frequency vibration to produce cavitation effect in the liquid in the oil tank and destroy the sludge structure. The combination of the two can effectively remove hard-to-reach dead corners and stubborn dirt.
Application details:
- Choose the right equipment: According to the size and shape of the oil tank, choose a handheld brush or a customized automatic cleaning device, supplemented by ultrasonic cleaning equipment.
- Process parameter control: Reasonably control the brushing time, vibration frequency and ultrasonic power to ensure thorough cleaning and prevent damage to the metal surface.
- Operation safety: During cleaning, ensure that the equipment is powered off and there is no residual oil in the oil tank to avoid accidents.
Chemical cleaning method
Principle and advantages:
- The chemical cleaning method triggers a chemical reaction in the fuel tank by adding a special cleaning agent to decompose the sludge and oxidized deposits. Its advantage is that it can deeply decompose stubborn deposits, and is particularly suitable for deep cleaning of heavily polluted fuel tanks.
Application details:
- Choose a low-corrosive cleaning agent: It must be ensured that the cleaning agent does not damage the fuel tank material and has a good dissolving effect on the sludge.
- Immersion time and reaction temperature: Set the soaking time of the cleaning agent in the fuel tank according to the degree of pollution, and use the appropriate temperature to accelerate the reaction.
- Subsequent thorough flushing: After chemical cleaning, high-pressure water flow or other methods must be used for thorough flushing to avoid chemical residues affecting the quality of subsequent oil products.
High-pressure water flow flushing and pneumatic assisted cleaning
Principle and advantages:
- High-pressure water flow flushing uses the impact force of the water flow to wash off the loose and partially stubborn dirt attached to the inner wall of the fuel tank. Combined with pneumatic assistance (such as air jet), the inside of the fuel tank can be cleaned from multiple angles, which is suitable for situations where the fuel tank design is more complex.
Application details:
- Segmented flushing: Due to the large space of the oil tank, it is recommended to flush in sections to ensure that each area can be fully impacted.
- Water quality requirements: Use clean water that has been softened to prevent minerals in the water from secondary contamination of the oil tank.
- Thorough drying: After flushing, professional equipment must be used for rapid drying to prevent residual moisture from causing metal corrosion.
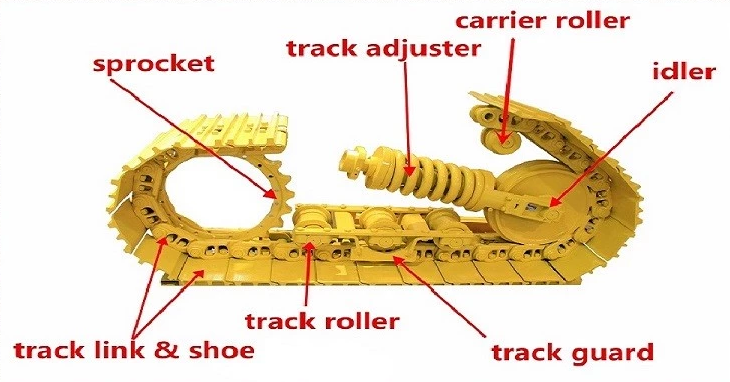
Detailed operation procedures and precautions for oil tank cleaning
To ensure that the cleaning process is both efficient and safe, the following is a set of systematic operation procedures and details to pay attention to:
Preliminary preparation and risk assessment
- Safety inspection: Confirm that the equipment has been powered off, shut down and cooled to prevent accidental scalding or electric shock accidents during the cleaning process.
- Tool and material preparation: Check whether the required tools (brushes, ultrasonic instruments, high-pressure flushing equipment, etc.) and cleaning agents meet the requirements.
- Environmental assessment: Select a well-ventilated site that meets environmental protection requirements, set up an oil collection device to prevent secondary contamination.
Oil draining and preliminary flushing
- Oil draining: Drain the oil in the oil tank into a dedicated storage container and do a preliminary separation of pollutants.
- Preliminary flushing: Use low-pressure water flow for pre-rinsing to remove loose contaminants on the surface and create conditions for subsequent deep cleaning.
Targeted cleaning implementation
- Chemical cleaning operation: According to the instructions of the cleaning agent, evenly inject it into the oil tank, let it stand for a period of time, and then use mechanical auxiliary tools to brush it.
- Mechanical/ultrasonic assistance: After chemical cleaning or using mechanical brushing and ultrasonic cleaning alone, repeatedly treat the inner wall and dead corners of the oil tank.
- High-pressure flushing: Use a high-pressure water gun to flush at multiple angles to ensure that the chemical cleaning agent and decomposed sludge are completely washed away.
Post-drying, inspection and restoration
- Thorough drying: Use industrial air drying equipment or heating system to completely evaporate the water in the oil tank to prevent residual water from causing subsequent corrosion.
- Quality inspection: Perform a comprehensive visual and instrument inspection on the inner wall of the oil tank, and restore it after confirming that there is no residual dirt.
- Restoration installation: Replace or clean the filter, re-inject oil that meets technical standards, and conduct a trial run inspection.
Environmental protection and safety records
- Waste oil and wastewater treatment: All discharged oil, cleaning agents and flushing water must be centrally processed and recorded in accordance with environmental protection requirements.
- Operation record archiving: Completely record the cleaning process, materials used, test data and equipment status to provide a basis for later maintenance and problem tracing.

Regular maintenance and preventive measures
A single deep cleaning can certainly solve the problem of oil tank dirt at the time, but establishing a long-term, systematic prevention and maintenance mechanism is the fundamental to ensure the long-term operation of the equipment.
Regular oil and filter testing
- Online monitoring system: Use oil quality sensors and online testing equipment to monitor oil viscosity, acid value, water content and suspended impurities in real time.
- Preventive replacement: According to the test data and equipment working environment, scientifically formulate the replacement cycle of oil and filters to prevent the spread of pollution.
Optimize the design of the filtration system
- Multi-stage filtration technology: Introduce primary, secondary and even tertiary filtration systems to improve the purification effect of oil products and reduce the risk of foreign impurities entering.
- Clean the filter regularly: Periodically clean and disinfect the washable filter to ensure that the filtration accuracy is not reduced due to blockage.
Fuel tank protection technology upgrade
- Inner wall coating and anti-rust treatment: Spray corrosion-resistant and easy-to-clean coating on the inside of the fuel tank or adopt lining design to reduce metal wear and deposition adhesion.
- Intelligent monitoring and early warning: Combined with the Internet of Things technology, the temperature, pressure and oil status of the fuel tank are monitored to timely warn of potential risks and achieve precise maintenance.
Regular training and standardized operation
- Personnel training: Regularly provide technical training and safety education to maintenance personnel to ensure that cleaning and maintenance operations comply with standard procedures.
- Establish a standard operating instruction (SOP): Develop detailed cleaning, testing, and maintenance processes to form a standardized operating system to reduce human errors.
Cutting-edge technology and future development trends
With the continuous advancement of engineering machinery technology, the field of fuel tank cleaning and maintenance is also constantly innovating. Some cutting-edge technologies are worth paying attention to:
- Automated cleaning system: Use robots and automatic spraying equipment to achieve fully automated and refined fuel tank cleaning, improve cleaning efficiency and uniformity.
- Nano antifouling coating: The new nano material coating has super oleophobic and antifouling properties, which is expected to fundamentally inhibit the formation of dirt.
- Data-driven maintenance: Based on big data and machine learning technology, the equipment operation data is analyzed to predict the trend of oil aging and tank pollution in advance, so as to achieve prevention first and maintenance second.
| Hızlı ve ücretsiz bir teklif alın | E-posta: henry@gfmparts.com | Whatsapp: +86 17705953659 |
The problem of excavator tank dirt involves multiple factors such as mechanical wear, chemical changes in oil products, water intrusion and filtration failure, forming a complex and dynamic pollution system. Through the organic combination of various cleaning methods such as regular oil drainage and oil change, physical and mechanical cleaning, chemical decomposition and high-pressure flushing, combined with systematic post-maintenance and monitoring measures, it is possible to achieve comprehensive treatment of tank dirt, extend equipment life, reduce operating risks, and save maintenance costs in long-term use.
In the future, with the continuous development of automation and intelligent technology and the popularization of nanomaterial applications, tank cleaning and maintenance technology will surely usher in new breakthroughs, bringing more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions to the heavy machinery industry.








